Detecting Danger: How Ultrasound Helps Identify Malignant Ovarian Cysts
Introduction
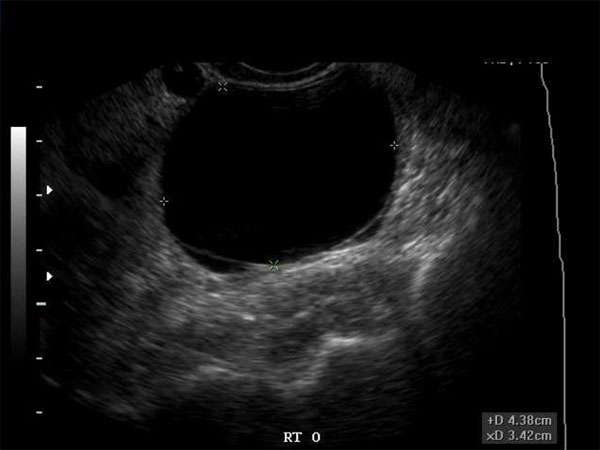
Ovarian cysts are a common occurrence in women of all ages. While most cysts are benign and resolve on their own, some can be malignant and pose a significant health risk. Timely detection and accurate diagnosis of malignant ovarian cysts are crucial in ensuring appropriate treatment and improving patient outcomes.
The Role of Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging plays a vital role in the detection and evaluation of ovarian cysts. By using sound waves to create images of the ovaries, ultrasound technology provides valuable information about the size, location, and characteristics of the cysts. This non-invasive imaging technique offers several advantages over other diagnostic methods, such as MRI or CT scans, including its accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and absence of ionizing radiation.
Identifying Malignancy
While ultrasound can detect the presence of ovarian cysts, distinguishing between benign and malignant cysts is challenging. However, certain ultrasound features can help sonographers and physicians in making a preliminary assessment of the cyst’s likelihood of malignancy. These features include:
-
- Irregular borders
- Multilocularity
- Thick septation
- Papillary projections
- Increased vascularity
If any of these features are present, further evaluation and intervention may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and plan appropriate treatment.
The Importance of Continuing Medical Education (CME)
Staying updated with the latest advancements in ultrasound technology and diagnostic criteria is essential for sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants involved in the evaluation of ovarian cysts. Continuing Medical Education (CME) programs offer professionals in these fields the opportunity to enhance their knowledge and skills, ensuring they provide the highest standard of care to their patients.
CME programs focusing on ovarian cyst evaluation using ultrasound can cover topics such as:
- Understanding the different types of ovarian cysts
- Recognizing ultrasound features suggestive of malignancy
- Interpreting ultrasound images accurately
- Applying the latest guidelines and recommendations
Requirements for CME
Each medical specialty and professional certification board may have specific CME requirements that need to be fulfilled. For example, the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) requires sonographers to complete a certain number of CME credits every three years to maintain their certification. Similarly, medical boards and associations have their own guidelines for CME for doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants.
It is crucial for healthcare professionals involved in the diagnosis and management of ovarian cysts to stay informed about the CME requirements relevant to their practice. By participating in accredited CME activities, professionals can enhance their skills, expand their knowledge, and ensure they meet the necessary educational standards to provide the best possible care to their patients.
Conclusion
Ultrasound imaging plays a crucial role in detecting and evaluating ovarian cysts, including the identification of potentially malignant cysts. By staying updated through ongoing CME, sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants can enhance their skills and knowledge, improving their ability to accurately diagnose and manage ovarian cysts. Continuous education ensures that healthcare professionals can provide the highest standard of care and ultimately contribute to better patient outcomes.
