A Closer Look at Hypoechoic Breast Lesions: Understanding the Risk Factors
Introduction
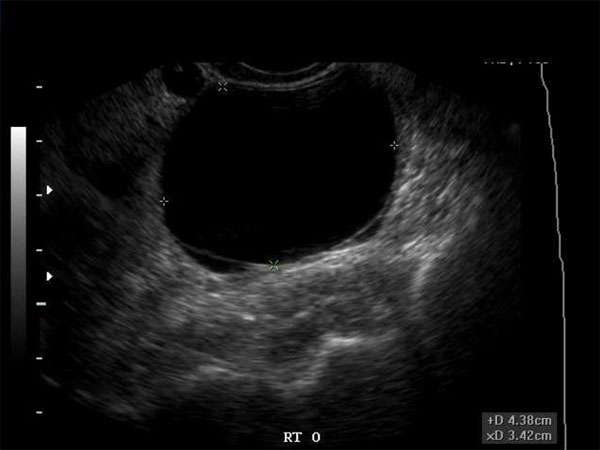
Hypoechoic breast lesions are a common finding during breast ultrasound examinations. These lesions, which appear darker than the surrounding breast tissue on ultrasound imaging, can be benign or malignant. Understanding the risk factors associated with hypoechoic breast lesions is crucial for early detection and effective management.
What are Hypoechoic Breast Lesions?
Hypoechoic breast lesions refer to areas within the breast that appear darker on ultrasound imaging. This darkness is an indication of increased density or stiffness compared to the surrounding breast tissue. While some hypoechoic lesions may be benign, others can be early signs of breast cancer.
Common Risk Factors
Several risk factors have been associated with hypoechoic breast lesions. It is important for healthcare professionals to be aware of these risk factors when evaluating patients. The following are some common risk factors:
- Age: Advanced age increases the risk of hypoechoic breast lesions.
- Family history: Having a close relative with a history of breast cancer can increase the likelihood of hypoechoic lesions.
- Prior breast cancer: Individuals with a history of breast cancer are at a higher risk of developing hypoechoic lesions.
- Hormonal factors: Hormonal imbalances, such as those seen in postmenopausal women, can contribute to the development of hypoechoic lesions.
The Importance of Continuing Medical Education (CME)
For healthcare professionals involved in breast imaging, staying up-to-date with the latest advancements and guidelines is essential. Continuing Medical Education (CME) plays a vital role in ensuring healthcare professionals maintain their knowledge and skills, ultimately improving patient care.
CME courses provide opportunities for sonographers, radiologists, OB/GYNs, vascular surgeons, emergency medicine physicians, family practice physicians, internal medicine physicians, orthopedic surgeons, sports medicine specialists, neurologists, cardiologists, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and other healthcare professionals to enhance their understanding of breast imaging techniques, risk assessment, and lesion characterization.
The Requirements for CME
Each healthcare profession has its own specific CME requirements. However, most require a specified number of CME credits to be earned within a certain time period. These credits can be obtained through attending conferences, workshops, online courses, and participating in research or educational activities.
For instance, the American College of Radiology (ACR) requires radiologists to earn a minimum of 75 CME credits over a three-year period. Similarly, the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ABOG) mandates OB/GYNs to complete 60 CME credits every three years.
Conclusion
Hypoechoic breast lesions are significant findings that require careful evaluation and management. Understanding the risk factors associated with these lesions can aid in early detection and timely intervention. Healthcare professionals involved in breast imaging should prioritize continuing medical education to stay updated with the latest advancements and guidelines. CME not only fulfills professional requirements but also ensures the delivery of high-quality patient care.