Detecting and Diagnosing Hypoechoic Breast Masses: A Review
Introduction
Hypoechoic breast masses are a common finding in diagnostic imaging studies. It is crucial for sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and other healthcare professionals to be well-versed in the detection and diagnosis of such masses. This article provides a comprehensive review of the subject, focusing on the importance of continuing medical education (CME) in staying updated with the latest advancements in this field.
What are Hypoechoic Breast Masses?
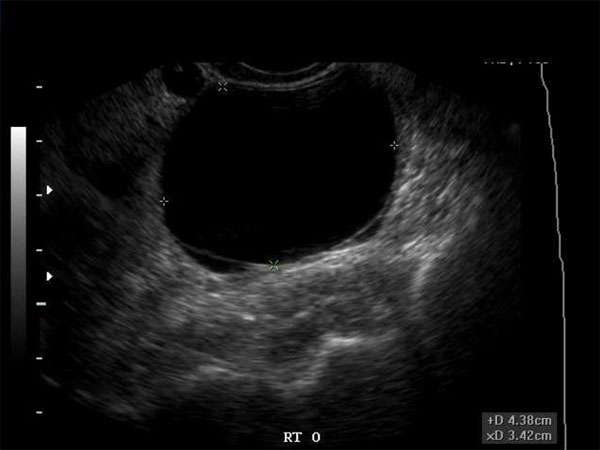
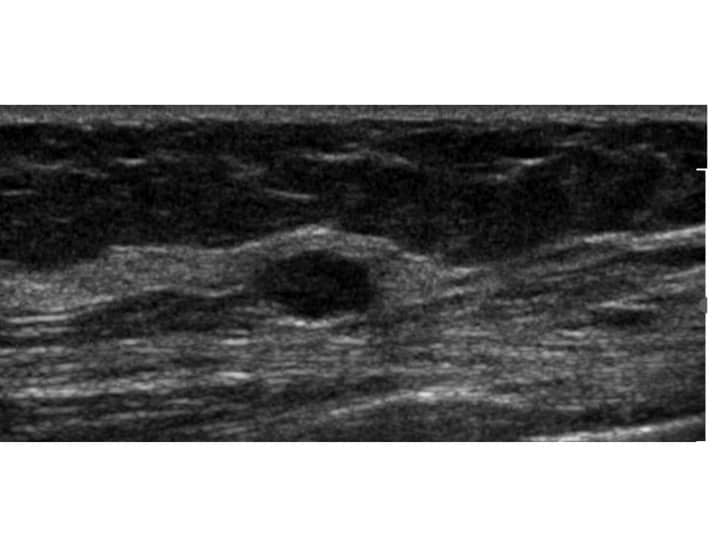
Hypoechoic breast masses are abnormal tissue formations within the breast that appear darker or less reflective on ultrasound imaging. These masses are often associated with breast cancer, although not all hypoechoic masses are malignant. Detecting and accurately diagnosing these masses is essential for timely intervention and treatment.
Diagnosing Hypoechoic Breast Masses
Diagnosing hypoechoic breast masses requires a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging techniques. Sonographers play a crucial role in performing ultrasound scans to identify and characterize these masses. Radiologists, OB/GYNs, vascular surgeons, and other specialists interpret the ultrasound images and provide a diagnosis or advise for the next step in management. This next step could be return to routine screening, observation, additional mammogram or MRI, or biopsy.
Importance of Continuing Medical Education (CME)
Continuing medical education (CME) is vital for healthcare professionals involved in breast imaging and diagnostics. CME courses and conferences provide opportunities to learn about new techniques, technologies, and research findings in the field of breast imaging. Staying updated with the latest advancements helps improve accuracy in detecting and diagnosing hypoechoic breast masses.
CME Requirements
The specific CME requirements vary depending on the healthcare professional’s specialty and jurisdiction. However, most regulatory bodies recommend a certain number of CME hours annually or within a specific time period. These requirements ensure that healthcare professionals maintain and enhance their knowledge and skills to provide the best possible care for their patients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, detecting and diagnosing hypoechoic breast masses is a crucial aspect of breast imaging and diagnostics. Sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and other healthcare professionals must stay updated with the latest advancements in this field through continuing medical education (CME). By fulfilling CME requirements, healthcare professionals can improve their expertise and provide better care to patients with breast masses.
To maintain your skills and stay up to date with the latest Breast imaging and management check our our Breast CME Section. Get unlimited CME each year for a very affordable price. Check out our premium courses that cover government and organizational required training.