Hypoechoic Breast Masses: An in-depth look at Imaging Techniques and Biopsy Procedures
Introduction
When it comes to breast health, early detection and accurate diagnosis are vital in ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients. Hypoechoic breast masses are a common finding during imaging examinations, and understanding the proper techniques for imaging and biopsy procedures is crucial for healthcare professionals involved in breast care.
Imaging Techniques for Hypoechoic Breast Masses
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in identifying and characterizing hypoechoic breast masses. Ultrasound is often the preferred modality due to its ability to provide real-time images and its non-invasive nature. Other imaging modalities such as mammography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) may also be used in specific cases.
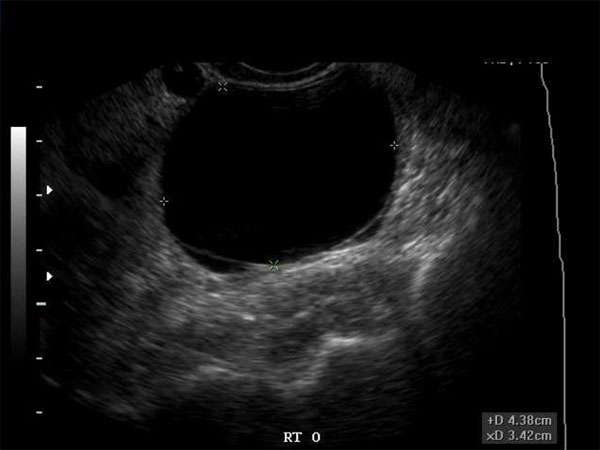
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound is the primary imaging technique used to assess hypoechoic breast masses. It utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the breast tissue. By analyzing the echogenicity and morphology of the mass, sonographers and radiologists can determine the likelihood of malignancy and guide further diagnostic steps.
Mammography
Mammography is commonly used in conjunction with ultrasound to evaluate hypoechoic breast masses. It provides detailed X-ray images of the breast tissue and can help identify calcifications and other suspicious features that may indicate malignancy.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is a powerful imaging technique used to assess breast masses, including hypoechoic lesions. It provides detailed images of the breast tissue using magnetic fields and radio waves. MRI is particularly useful in cases where ultrasound and mammography results are inconclusive or when assessing high-risk patients.
Computed Tomography (CT)
In some cases, CT scans may be utilized to evaluate hypoechoic breast masses. CT scans use X-rays and computer processing to create cross-sectional images of the breast tissue. However, CT scans are typically not the first-line imaging modality for breast masses and are reserved for specific indications.
Biopsy Procedures for Hypoechoic Breast Masses
Once a hypoechoic breast mass has been identified, a biopsy procedure is often necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine appropriate treatment plans. There are several biopsy techniques available, each with its advantages and considerations.
Ultrasound-Guided Core Needle Biopsy
Ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure that uses ultrasound imaging to guide the biopsy needle into the targeted mass. It allows for accurate sampling of the tissue for histological analysis without significant discomfort for the patient.
Stereotactic Biopsy
Stereotactic biopsy is typically used when the mass is not well visualized on ultrasound or when suspicious calcifications are present. This procedure uses mammography or MRI guidance to precisely target the suspicious area and obtain tissue samples for analysis.
Surgical Biopsy
In certain cases, surgical biopsy may be necessary to obtain a definitive diagnosis. This procedure involves the removal of the entire mass or a portion of it through surgery. Surgical biopsies are typically performed under general anesthesia and require a longer recovery period.
Continuing Medical Education (CME) Requirements and Importance
For healthcare professionals involved in breast care, staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in imaging techniques and biopsy procedures is essential. Continuing Medical Education (CME) programs provide opportunities for professionals to enhance their knowledge and skills, ensuring the delivery of high-quality patient care.
Requirements for CME vary depending on the profession and jurisdiction. However, it is generally recommended that healthcare professionals obtain a certain number of CME credits annually or within a specific time frame to maintain their licensure and demonstrate competence in their field.
The importance of CME cannot be overstated. Advances in technology and research continuously shape the field of breast imaging and biopsy procedures. By participating in CME activities, healthcare professionals can stay informed about emerging techniques, best practices, and evidence-based guidelines, ultimately improving patient outcomes and safety.
Furthermore, CME provides an opportunity for healthcare professionals to network with colleagues, share experiences, and engage in discussions that foster professional growth and collaboration. By actively participating in CME, healthcare professionals can contribute to the advancement of their field and provide the best possible care for their patients.
Conclusion
Hypoechoic breast masses require careful evaluation through appropriate imaging techniques and biopsy procedures. Ultrasound is the primary imaging modality, while techniques such as ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy and stereotactic biopsy are commonly used for obtaining tissue samples. Staying current with CME requirements is essential for healthcare professionals involved in breast care to ensure optimal patient outcomes and maintain professional competence.