Ultrasound Imaging: Differentiating Between Benign and Malignant Ovarian Cysts
Introduction
Ultrasound imaging plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of ovarian cysts. Ovarian cysts are common findings in women of all ages and can be either benign or malignant. Accurate differentiation between the two is essential to determine appropriate treatment strategies. In this article, we will explore the role of ultrasound imaging and its importance in distinguishing between benign and malignant ovarian cysts.
Understanding Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop within or on the surface of the ovaries. They can vary in size, ranging from as small as a pea to as large as a grapefruit. While most ovarian cysts are benign and resolve on their own, some may require medical intervention due to their potential to become malignant or cause complications.
The Role of Ultrasound Imaging
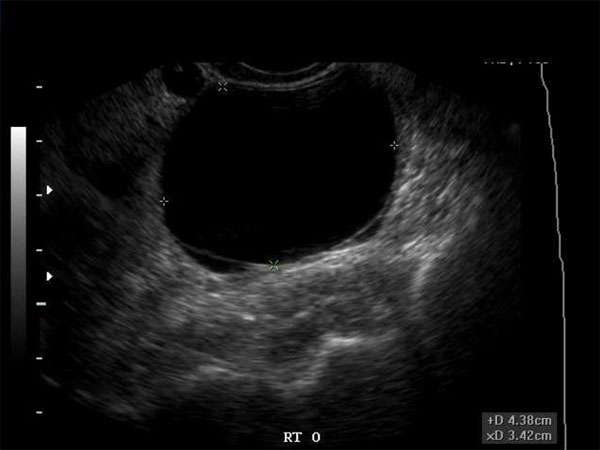
Ultrasound imaging, also known as sonography, is a non-invasive and safe imaging technique that utilizes sound waves to create real-time images of the internal structures of the body. When it comes to evaluating ovarian cysts, ultrasound is the imaging modality of choice.
Ultrasound allows for detailed visualization of the size, location, and characteristics of ovarian cysts. It can help determine the nature of the cyst, whether it is solid or filled with fluid. Additionally, ultrasound can assess the blood flow within the cyst, which aids in distinguishing between benign and malignant cysts.
Differentiating Benign and Malignant Ovarian Cysts
While ultrasound imaging provides valuable information about ovarian cysts, differentiating between benign and malignant cysts can be challenging. However, certain characteristics can help in making a more accurate diagnosis:
1. Shape and Contour
Benign cysts typically have smooth, regular shapes and well-defined borders, whereas malignant cysts may exhibit irregular shapes and irregular borders.
2. Internal Structure
Benign cysts often have a homogeneously fluid-filled appearance, while malignant cysts may contain solid components or septations within the fluid-filled sac.
3. Blood Flow
Assessing the blood flow within the cyst using Doppler ultrasound can provide valuable information. Benign cysts usually demonstrate minimal or no blood flow, while malignant cysts may exhibit increased vascularity.
4. Growth Rate
Monitoring the growth rate of the cyst over time is crucial. Benign cysts tend to remain stable in size or may even shrink, while malignant cysts often show rapid growth.
The Importance of Continuing Medical Education (CME)
For sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants involved in ultrasound imaging, continuous learning and staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in the field are essential. Continuing Medical Education (CME) programs provide professionals with the opportunity to enhance their knowledge and skills.
CME courses specifically focusing on ultrasound imaging of ovarian cysts can help healthcare providers improve their ability to differentiate between benign and malignant cysts accurately. These courses cover the latest techniques, guidelines, and research findings, equipping professionals with the necessary tools to provide optimal patient care.
Conclusion
Ultrasound imaging plays a vital role in differentiating between benign and malignant ovarian cysts. By assessing various characteristics such as shape, internal structure, blood flow, and growth rate, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions regarding treatment and management. Continuous learning through CME programs ensures that sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants stay updated with the latest advancements in ultrasound imaging, enabling them to provide the best possible care for their patients.