Understanding Ovarian Cysts: Identifying the Difference Between Benign and Malignant on Ultrasound
As a sonographer or medical professional in the fields of radiology, obstetrics and gynecology, emergency medicine, family practice, internal medicine, or as a nurse practitioner or physician assistant, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of ovarian cysts. These fluid-filled sacs that develop within or on the surface of the ovaries can be a common finding during ultrasound examinations. However, distinguishing between benign and malignant cysts is of utmost importance for accurate diagnosis and appropriate patient management.
Importance of Ultrasound in Identifying Ovarian Cysts
Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that utilizes sound waves to produce real-time images of the body’s internal structures. It is a valuable tool for visualizing and characterizing ovarian cysts due to its ability to provide detailed information about their size, shape, location, and composition.
By using ultrasound, sonographers and medical professionals can differentiate between simple cysts, which are usually benign and resolve on their own, and complex cysts, which may have a higher risk of malignancy. Complex cysts often exhibit features such as solid components, septations, thickened walls, or irregular shapes, raising concerns for potential malignancy.
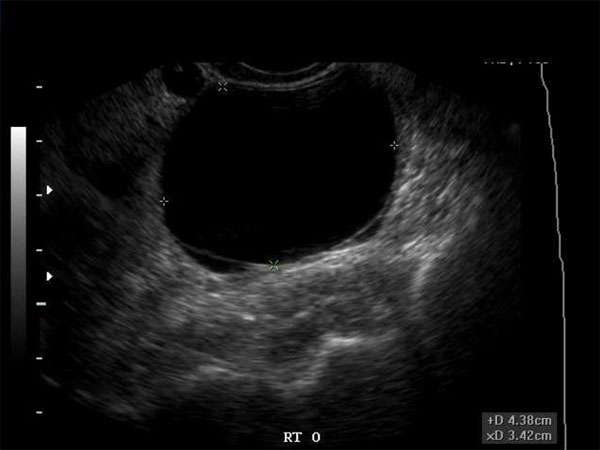
Distinguishing Benign from Malignant Cysts on Ultrasound
To accurately identify the nature of an ovarian cyst, sonographers and medical professionals should pay attention to specific ultrasound characteristics. These characteristics can help differentiate between benign and malignant cysts:
1. Size
Benign cysts are typically smaller, with a diameter of less than 5 centimeters. Malignant cysts, on the other hand, tend to be larger, often exceeding 5 centimeters.
2. Shape and Contour
Benign cysts often appear as well-defined, rounded structures with smooth contours. Malignant cysts may exhibit irregular shapes and have an irregular or nodular contour.
3. Internal Echoes
Benign cysts are usually filled with clear fluid, resulting in anechoic or hypoechoic appearances on ultrasound. Malignant cysts, however, may contain solid components or debris, leading to increased echogenicity or the presence of echogenic nodules.
4. Septations and Wall Thickness
Simple, benign cysts generally do not have internal septations or thickened walls. In contrast, complex cysts with multiple septations or thickened walls may suggest a higher risk of malignancy.
The Importance of Continuing Medical Education (CME)
For sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants, staying up to date with the latest advancements, techniques, and guidelines in the field is crucial. Continuing Medical Education (CME) provides healthcare professionals with the opportunity to enhance their knowledge and skills, ensuring they deliver the highest quality of care to their patients.
CME requirements vary depending on the profession and licensing board, but they typically involve completing a certain number of educational activities, such as attending conferences, workshops, webinars, or completing online courses. These activities focus on topics related to the healthcare professional’s field of practice, ensuring they remain competent and knowledgeable in their respective specialties.
By actively participating in CME activities, sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants can stay updated on the latest advancements in ultrasound imaging, including the identification and management of ovarian cysts. This ongoing education not only benefits the healthcare professional but also improves patient outcomes by enabling accurate diagnoses and appropriate treatment plans.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between benign and malignant ovarian cysts on ultrasound is crucial for sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants involved in the care of patients. By staying up to date with the latest advancements through CME, healthcare professionals can ensure accurate identification and appropriate management of ovarian cysts, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.