Decoding Ovarian Cysts: Distinguishing Between Benign and Malignant on Ultrasound
Introduction
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on the ovaries. While most ovarian cysts are benign and resolve on their own, it is crucial for healthcare professionals, especially sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants, to accurately distinguish between benign and malignant cysts to provide appropriate patient management and care.
Ultrasound Imaging: A Powerful Diagnostic Tool
Ultrasound imaging plays a vital role in the evaluation of ovarian cysts. It allows healthcare professionals to assess the size, location, composition, and characteristics of the cysts. By utilizing specific ultrasound techniques and features, sonographers and doctors can differentiate between benign and malignant cysts.
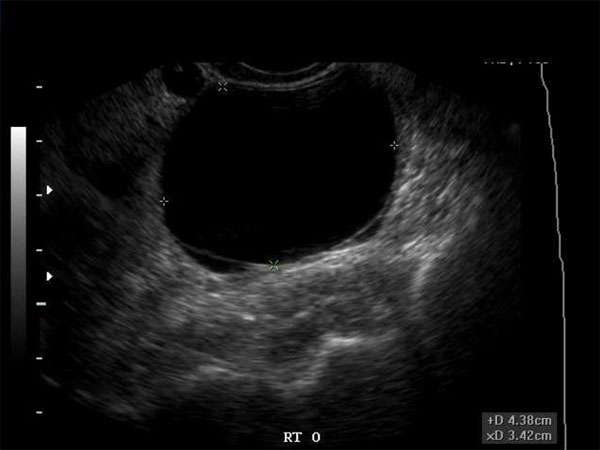
Key Ultrasound Features for Distinguishing Between Benign and Malignant Cysts
1. Shape and contour: Benign cysts tend to have smooth, rounded contours, while malignant cysts may exhibit irregular shapes and irregular borders.
2. Echogenicity: Benign cysts often appear anechoic or hypoechoic, meaning they have few or no internal echoes. Malignant cysts, on the other hand, may have internal echoes, septations, or solid components, making them more echogenic.
3. Fluid characteristics: Benign cysts typically contain clear or straw-colored fluid, whereas malignant cysts may contain blood, debris, or thick, viscous fluid.
4. Wall thickness: Benign cysts usually have thin walls, whereas malignant cysts often have thickened walls.
5. Color Doppler analysis: Utilizing color Doppler ultrasound can help evaluate the vascularity of the cysts. Benign cysts are usually avascular or have minimal blood flow, while malignant cysts may exhibit increased blood flow or the presence of vascular structures.
The Importance of Continuing Medical Education (CME)
As medical knowledge and technology rapidly advance, healthcare professionals must stay updated with the latest developments in their field. Continuing medical education (CME) plays a critical role in ensuring that sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants possess the necessary skills and knowledge to provide the best possible care to their patients.
Requirements for CME
Specific CME requirements vary depending on the profession and jurisdiction. Sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants must fulfill these requirements to maintain their licenses and certifications. CME activities may include attending conferences, workshops, webinars, or online courses that focus on topics relevant to their practice, such as ultrasound imaging and the diagnosis of ovarian cysts.
Benefits of CME
1. Enhanced patient care: By staying updated with the latest advancements in their field, healthcare professionals can provide more accurate diagnoses and develop appropriate treatment plans for patients with ovarian cysts.
2. Improved professional competence: CME ensures that healthcare professionals continuously expand their knowledge, refine their skills, and enhance their ability to provide quality care.
3. Networking and collaboration: CME activities often provide opportunities for healthcare professionals to connect with peers, exchange ideas, and collaborate on research or clinical projects.
4. Professional growth and career advancement: Continuous learning through CME can open doors to new career opportunities, leadership roles, and specialization within the field of sonography, radiology, OB/GYN, emergency medicine, family practice, or internal medicine.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between benign and malignant ovarian cysts is crucial for healthcare professionals involved in the diagnosis and management of these conditions. Ultrasound imaging, with its specific features and techniques, plays a vital role in accurately identifying and differentiating between these cysts. Furthermore, continuing medical education (CME) is essential for sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants to stay updated with the latest advancements in their field and provide the best possible care to their patients.