Hypoechoic Breast Masses: An Overview of Imaging Techniques and Interpretation
Introduction
Hypoechoic breast masses are a common finding in medical imaging, particularly in mammography and ultrasound examinations. These masses appear darker compared to surrounding tissues due to their ability to reflect less sound waves. This article aims to provide an overview of imaging techniques used to detect and interpret hypoechoic breast masses.
Imaging Techniques
Several imaging techniques are commonly used to evaluate hypoechoic breast masses, including mammography, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Each modality offers unique advantages and can provide valuable information for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Mammography
Mammography is a low-dose X-ray imaging technique that can detect abnormalities in breast tissue, including hypoechoic masses. It is commonly used as a screening tool for breast cancer detection. Mammograms can provide detailed images of breast structures, allowing radiologists to identify and assess the characteristics of hypoechoic masses.
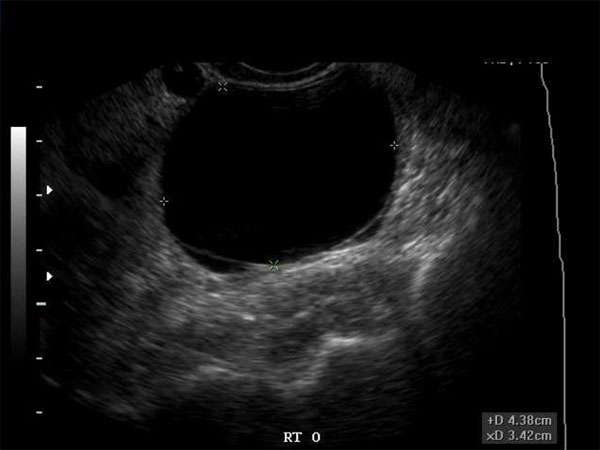
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of breast tissue. It is a non-invasive, safe, and cost-effective technique that is commonly used for evaluating breast masses. Hypoechoic masses can be easily detected on ultrasound, and additional features such as shape, margins, and vascularity can be assessed, aiding in the diagnosis and classification of the mass.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is a powerful imaging technique that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of breast tissue. It is often used as a supplemental tool for further evaluation of hypoechoic breast masses detected on mammography or ultrasound. MRI can provide additional information about the extent and characteristics of the mass, helping in the assessment of malignancy and treatment planning.
Interpretation
The interpretation of hypoechoic breast masses requires knowledge and expertise in breast imaging. Sonographers, radiologists, OB/GYNs, and other healthcare professionals must carefully analyze the imaging findings, considering the patient’s clinical history and risk factors. Characteristics such as size, shape, margins, echogenicity, and vascularity are important factors in determining the likelihood of malignancy.
Continuing Medical Education (CME)
Continuing medical education (CME) plays a crucial role in ensuring healthcare professionals stay up-to-date with the latest advancements and guidelines in breast imaging. CME activities, such as conferences, workshops, and online courses, provide opportunities to enhance knowledge and skills in interpreting hypoechoic breast masses. It is important for healthcare professionals to actively engage in CME to provide the best possible care for their patients.
Importance of CME
Regular participation in CME activities is essential for healthcare professionals involved in breast imaging. Advances in imaging technology, evolving guidelines, and new research findings necessitate ongoing education to maintain proficiency in interpreting hypoechoic breast masses. CME enables healthcare professionals to enhance their diagnostic accuracy, improve patient outcomes, and stay updated with the latest evidence-based practices.
Conclusion
Hypoechoic breast masses are frequently encountered in medical imaging, and accurate interpretation is vital for appropriate patient management. Mammography, ultrasound, and MRI are valuable imaging techniques used to detect and evaluate these masses. Continuing medical education is essential for healthcare professionals to stay current with evolving techniques and guidelines to provide optimal care for patients with hypoechoic breast masses.