Hypoechoic Breast Masses: What Women Need to Know
Introduction
As a woman, it is essential to be aware of any changes or abnormalities in your breasts. One such abnormality that may be detected during a breast ultrasound is a hypoechoic breast mass. This article aims to provide valuable information about hypoechoic breast masses, their significance, and what steps women should take if they encounter one.
Understanding Hypoechoic Breast Masses
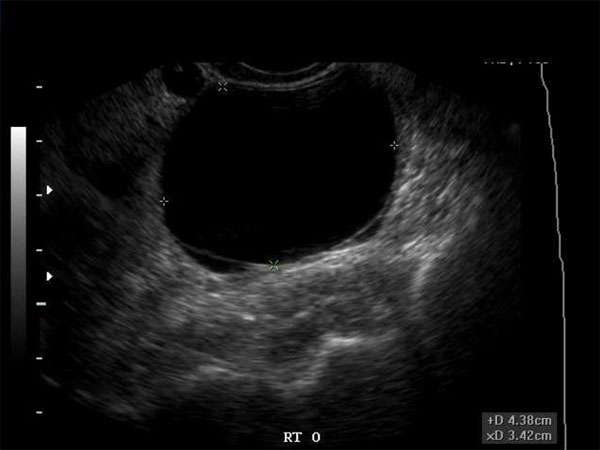
A hypoechoic breast mass refers to an area in the breast that appears darker or less echoic compared to the surrounding breast tissue on an ultrasound. These masses can be benign or malignant and require further evaluation to determine their nature accurately. Benign hypoechoic masses are usually harmless and may include cysts, fibroadenomas, or other non-cancerous growths. However, malignant hypoechoic masses could indicate the presence of breast cancer.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of breast abnormalities, including hypoechoic masses, is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Regular breast self-examinations, along with routine mammograms and clinical breast examinations, can aid in identifying any changes in breast tissue. If a hypoechoic mass is detected during these screenings, further imaging tests such as a breast ultrasound or MRI may be recommended to evaluate its characteristics and determine the appropriate course of action.
Role of Sonographers and Healthcare Professionals
Sonographers, radiologists, OB/GYNs, and various other healthcare professionals play a significant role in the detection and diagnosis of hypoechoic breast masses. Their expertise in performing and interpreting breast ultrasounds allows for accurate identification of these masses and guides subsequent treatment decisions. Continuing Medical Education (CME) is essential for healthcare professionals to stay updated with the latest advancements and techniques in breast imaging, enabling them to provide the highest quality care to their patients.
The Importance of Continuing Medical Education (CME)
Continuing Medical Education (CME) is a vital component of professional growth for healthcare professionals. It ensures that they remain knowledgeable about the latest research, technologies, and best practices in their respective fields. CME also helps physicians and other healthcare professionals maintain their licensure and certification requirements. Attending CME courses, conferences, and workshops focused on breast imaging and breast pathology can enhance their skills in detecting and diagnosing hypoechoic breast masses accurately.
Requirements for CME
The specific requirements for CME vary depending on the healthcare professional’s specialty and the governing board of their profession. However, most boards require a certain number of CME credits to be earned within a specified time frame. These credits can be obtained by attending accredited CME programs, participating in online courses, workshops, or conferences. Healthcare professionals should familiarize themselves with the CME requirements of their respective boards to ensure compliance.
Conclusion
Hypoechoic breast masses can be a cause for concern, but early detection and accurate diagnosis are key to effective treatment. Women should be proactive in conducting regular breast self-examinations and undergoing recommended screenings. Healthcare professionals, including sonographers and doctors, should prioritize continuing medical education to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in breast imaging and effectively diagnose hypoechoic masses. By working together, we can ensure better outcomes for women facing breast abnormalities.