Hypoechoic Breast Masses: Characteristics, Diagnosis, and Treatment Approaches
Introduction
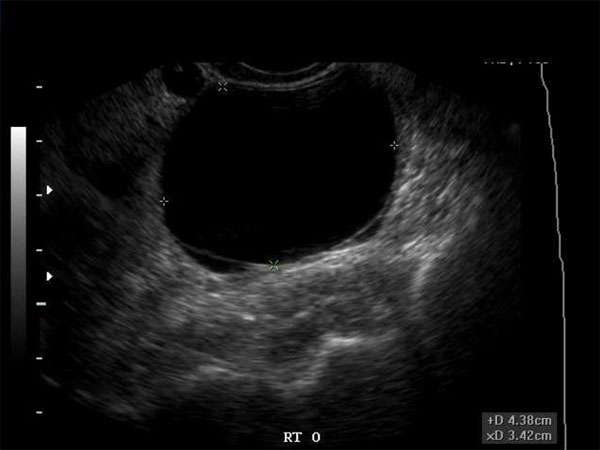
Hypoechoic breast masses refer to abnormal areas in the breast that appear darker or less echogenic on ultrasound imaging. These masses are of significant concern as they can be indicative of breast cancer or other serious conditions. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, diagnosis, and treatment approaches for hypoechoic breast masses.
Characteristics of Hypoechoic Breast Masses
Hypoechoic breast masses are typically characterized by their darker appearance on ultrasound imaging. They appear as solid masses and may exhibit irregular borders. These masses often have increased vascularity and can be associated with microcalcifications. It is important to note that not all hypoechoic masses are cancerous, but they require further evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
Diagnosis of Hypoechoic Breast Masses
Accurate diagnosis of hypoechoic breast masses requires a combination of imaging techniques and clinical evaluation. Ultrasound is the primary imaging modality used to assess breast masses. Additional imaging such as mammography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be recommended based on the initial findings. The use of ultrasound-guided biopsy or fine-needle aspiration may be necessary to obtain tissue samples for histopathological analysis.
Treatment Approaches for Hypoechoic Breast Masses
The treatment approach for hypoechoic breast masses depends on the underlying cause and the presence of malignancy. If the mass is found to be benign, a watchful waiting approach may be adopted, with regular monitoring through imaging. If the mass is suspicious for malignancy, further interventions such as surgical excision or targeted therapy may be recommended. The specific treatment plan will be tailored to the individual patient’s needs and preferences, and may involve a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals.
Continuing Medical Education (CME) Requirements
For sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and other healthcare professionals involved in breast imaging, staying up to date with the latest developments is crucial. Continuing Medical Education (CME) is essential to maintain and enhance professional competence and knowledge. CME courses and conferences provide opportunities to learn about advancements in breast imaging techniques, interpretation skills, and treatment approaches. By participating in CME activities, healthcare professionals can ensure they are delivering the best possible care to their patients.
The Importance of CME in Breast Imaging
Breast imaging is a rapidly evolving field with new technologies, guidelines, and research emerging regularly. CME allows healthcare professionals to stay current with these advancements, ensuring accurate and timely diagnosis of breast abnormalities. CME also promotes the adoption of best practices, improves patient outcomes, and enhances patient safety. By investing time and effort into CME, healthcare professionals can maintain their competency and contribute to the overall improvement of breast imaging services.
In Conclusion
Hypoechoic breast masses are significant findings that require thorough evaluation and appropriate management. Through accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment approaches, healthcare professionals can ensure the best possible outcomes for patients. Additionally, participating in CME activities is essential for staying up to date with the latest advancements in breast imaging and maintaining professional competence. By prioritizing CME, healthcare professionals can provide optimal care and contribute to the continuous improvement of breast imaging practices.