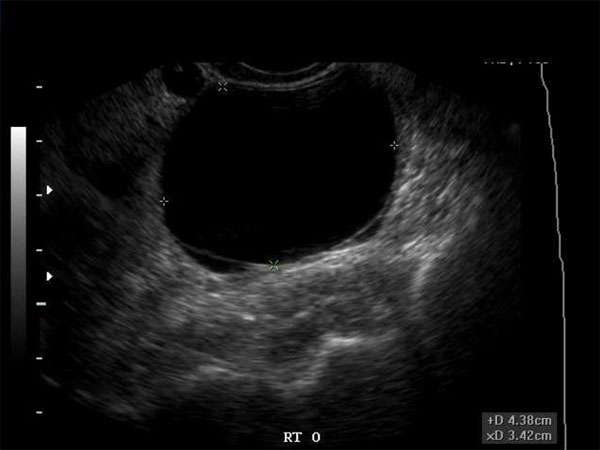
Hypoechoic Masses in the Breast: Signs, Symptoms, and Diagnostic Techniques
Introduction
Hypoechoic masses in the breast are a common finding in medical imaging. They can be an indication of various conditions, including benign or malignant tumors. It is crucial for healthcare professionals, especially sonographers and doctors, to understand the signs, symptoms, and diagnostic techniques associated with hypoechoic masses in the breast.
Signs and Symptoms
Patients with hypoechoic masses in the breast may present with several signs and symptoms. These can include a palpable lump, breast pain, nipple discharge, changes in breast size or shape, skin changes, or swollen lymph nodes in the armpit area. It is important to note that not all patients will exhibit these symptoms, and some hypoechoic masses may be asymptomatic.
Diagnostic Techniques
Proper diagnosis of hypoechoic masses in the breast often involves a combination of imaging techniques and procedures. The primary diagnostic tool is ultrasound, which can provide detailed images of the breast tissue and help differentiate between solid masses and cysts. Other imaging modalities, such as mammography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT), may also be used to obtain a more comprehensive view.
In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to determine the nature of the hypoechoic mass. This can involve needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, or surgical excision. The extracted tissue is then sent for pathological analysis, which can confirm whether the mass is benign or malignant.
Importance of Continuing Medical Education (CME)
For healthcare professionals, staying up to date with the latest advancements and techniques in diagnosing and managing hypoechoic masses in the breast is crucial. Continuous learning through Continuing Medical Education (CME) provides an opportunity to enhance knowledge, improve clinical skills, and ensure the delivery of quality patient care.
Medical professionals, including sonographers, radiologists, OB/GYNs, vascular surgeons, and other specialists, can fulfill their CME requirements by attending conferences, workshops, webinars, or completing online courses specifically tailored to breast imaging and pathology. CME enables healthcare professionals to stay current with emerging research, diagnostic guidelines, and treatment options for hypoechoic masses in the breast.
Additionally, CME allows healthcare professionals to collaborate and exchange knowledge with their peers, fostering a multidisciplinary approach to patient care. By participating in CME activities, healthcare professionals can ensure they are providing the highest level of care to patients with hypoechoic masses in the breast.
Conclusion
Hypoechoic masses in the breast require prompt evaluation and accurate diagnosis. Healthcare professionals, such as sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants, need to be well-versed in the signs, symptoms, and diagnostic techniques associated with these masses. Continuous learning through CME is essential for staying updated on the latest advancements in breast imaging and pathology, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.