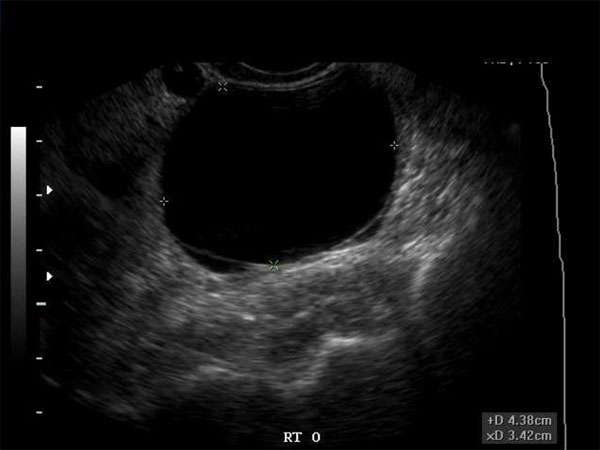
Understanding Hypoechoic Breast Masses: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Introduction
Hypoechoic breast masses are a common finding in ultrasound imaging and can raise concerns about potential breast cancer. It is crucial for healthcare professionals, including sonographers, doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants, to have a comprehensive understanding of the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for hypoechoic breast masses.
Causes of Hypoechoic Breast Masses
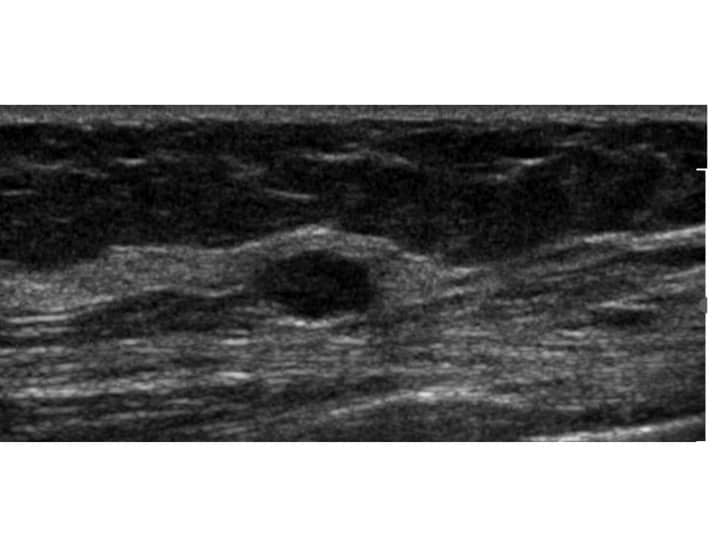
Hypoechoic breast masses can be caused by various factors, including:
-
- Breast cysts
-
- Fibroadenomas
-
- Intraductal papillomas
-
- Breast abscesses
-
- Breast cancer
Each of these causes requires specific diagnostic approaches and treatment strategies.
Diagnosis of Hypoechoic Breast Masses
Accurate diagnosis of hypoechoic breast masses is vital for determining the appropriate course of action. Diagnostic methods commonly used include:
-
- Ultrasound imaging
-
- Mammography
-
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
-
- Biopsy
These diagnostic techniques help healthcare professionals differentiate between benign and malignant masses, providing valuable information for treatment decisions.
Treatment Options
The treatment options for hypoechoic breast masses depend on the underlying cause. Some possible treatment approaches include:
-
- Observation and monitoring
-
- Aspiration or drainage of cysts
-
- Surgical removal of fibroadenomas or intraductal papillomas
-
- Antibiotic therapy for breast abscesses
-
- Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery for breast cancer
The choice of treatment is determined by factors such as the size, location, and characteristics of the mass, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences.
Continuing Medical Education (CME) Requirements
Healthcare professionals, especially those involved in breast imaging and diagnosis, should prioritize Continuing Medical Education (CME) to stay up to date with the latest advancements and best practices. CME courses provide opportunities to enhance knowledge and skills, ensuring the delivery of high-quality patient care.
The Importance of CME
CME plays a crucial role in maintaining competence and improving patient outcomes. By participating in CME activities, healthcare professionals can:
-
- Stay informed about the latest research and developments in breast imaging
-
- Learn new techniques for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning
-
- Understand emerging technologies and their applications in breast healthcare
-
- Network with peers and experts in the field
-
- Meet licensing and certification requirements
It is essential for healthcare professionals to regularly engage in CME activities to ensure optimal patient care and professional growth.
Conclusion
Understanding hypoechoic breast masses is vital for healthcare professionals involved in breast imaging and diagnosis. By staying updated on the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for hypoechoic breast masses, healthcare professionals can provide accurate assessments and appropriate care for their patients. Moreover, prioritizing Continuing Medical Education (CME) ensures ongoing professional development and the highest standard of patient care.